Dental problems in children
Dental problems in children that can often be seen at the dentist:
• Dental caries
• Gum disease
• tooth erosion
• Sensitive teeth
• Malocclusion
• Thumb sucking
• tongue pressure
dental caries
After colds, dental caries is one of the most common complaints not only in children, but also in adolescents and adults in the United States. This problem is due to the formation of plaque on the teeth.
Dental plaque is a sticky film that covers the teeth. It is created by the combination of bacteria and the acid that they release when processing sugar, food residues and saliva.
Gum disease
This gum infection, also known as periodontitis, begins with the formation of plaque.
This sticky film is removed from your teeth by brushing your teeth, but reappears within 24 hours.
If it is present for more than 2 or 3 days, it becomes a more stubborn crust that forms under the gum line.
This is called tartar, which can only be removed by tooth cleaning. Simply brushing your teeth and using dental floss are not enough.
Tartar is a good breeding ground for bacteria. Therefore, over time, it leads to an inflammation of the gums called gingivitis.
tooth erosion
This dental problem is also known as acid erosion and is becoming increasingly common in children and adults.
Products such as fruit juices and carbonated drinks are naturally acidic, and drinking too much of these substances can erode the tooth enamel.
Nocturnal bruxism means grinding your teeth. In children who suffer from this disorder, the affected tooth area can erode.
Sensitive teeth
Another common dental problem in children is increased tooth sensitivity.
As the name suggests, this disease of one or more teeth causes discomfort with hot or cold food and drinks.
malocclusion
Malocclusion is simply a misalignment of the teeth that leads to a false bite.
Children are more prone to this condition.
tongue print
Like thumb sucking, tongue pressure can be seen as a common dental problem in children.
The tongue is in the wrong position when swallowing.
Like thumb sucking, this process can put pressure on the teeth, causing them to lose their correct alignment.
Sometimes bite injuries or speech problems can occur.
Does my child need braces or not?
When does a child need braces?
There is no specific time when a child could need braces.
The orthodontist usually recommends a check-up at the age of 7.
Since the permanent teeth erupt from the age of 6 years, the orthodontist can identify slight problems with jaw growth and erupting teeth.
Early detection and treatment prevents future problems and creates suitable conditions for the pre-breaking and growth of the permanent teeth.
Food can get caught in the braces and it takes a lot of effort for the children to brush their teeth.
Children with braces must also avoid certain hard foods, sticky candies, popcorn and chewing gum.
These could get caught in the braces and cause damage.
Why do children need braces??
There are some signs that will help the orthodontist decide whether the child needs braces. This includes:
Most children need braces on average for two years.
Yellow teeth in children, causes and remedies
Thin enamel
One of the most common and poorly diagnosed causes of yellowed teeth is the presence of thin enamel.
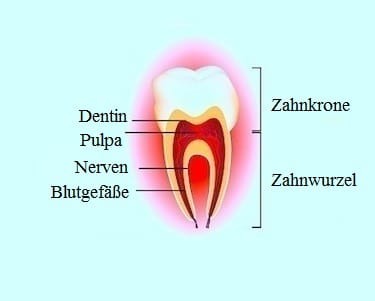
The enamel is the outermost layer of teeth and is not only the hardest structure of the human body, but also the substance that gives teeth their white color. Under the enamel is the dentin (dentine), which is somewhat yellowish and also sensitive to heat and cold.
Some children naturally have a very thin layer of enamel or the enamel has become thinner due to food, excessive brushing or carbonated drinks. In this case, it is not the yellowish color, but the dentin that shines through the tooth.
stains
Some children brush their teeth very poorly, which can lead to yellow teeth.
As a result, they struggle with plaque and tartar.
This is often seen in children with braces, since correct dental hygiene is often not easy with these devices.
When using braces, brushing your teeth twice a day is not enough.
The person concerned should go to the dentist for teeth cleaning and have the substances removed that settle on the tooth surface.
Medicines: internal and external stains
There are some medications that stain teeth. They can cause internal or external stains on the teeth, yellowing or black spots can occur.
The main responsible for this include tetracyclines.
Tetracyclines are antibiotics that are used to treat various infections and fevers.
One of the main side effects of tetracyclines is that they cause teeth yellowing in children.
In fact, studies have shown that when tetracycline is used in pregnant women, the broken teeth of the child may be affected.
Black teeth, causes and treatment
Black teeth can be a very uncomfortable and unaesthetic disorder.
Poor oral hygiene
One of the most common causes of black teeth is oral hygiene. In today’s hectic world, maintaining dental hygiene and dental health often becomes an unimportant issue.
For example, people do not brush their teeth regularly or delay a visit to the dentist until toothache becomes unbearable.
If you do not keep your mouth clean, plaque and tartar form on your teeth.
When you drink coffee or sugary drinks, they deposit on your teeth and they slowly turn black. This is a major cause of black teeth in children.
Teeth can also turn gray, matte, or brown due to fungi and bacteria growing on the tooth surface.
dental caries
The second most common cause of black teeth is dental caries.
If a person does not brush their teeth regularly, bacteria will get stuck in the interdental spaces or the grooves and cracks on the tooth surface.
At first, it can look like a light brownish depigmentation (discoloration).
However, if the tooth structure continues to lose minerals, the caries slowly softens and causes black teeth.
If caries is not treated in this phase, it can penetrate to the dentin and pulp and cause pain and swelling.
White spots on milk teeth
White spots can be caused by fluorosis, which is an excess of fluorine in the blood due to diet or supplements.
If the patient does not change the diet, he risks creating cavities or grooves in the teeth.
When does teething begin in children?
When do the milk teeth break out? How many?
It is very difficult to make a prediction about teething in children. There are no applicable parameters to accurately predict how long it will take for the child to start teething.
Children are born with 20 milk teeth.
These teeth are hidden under the gums and are waiting to come out, generally the first teeth appear after about 6 months and the last (molars) after about 30 months.
The crucial phase for teething
This phase begins between the 4th and 7th month. Teething in children 4 months of age is rare, but not impossible.
The lack of teeth in a child of about 9 months is not uncommon.
Most children have a single tooth smile when they are about 6 months old.
Some symptoms of falling teeth are mild discomfort, loss of appetite, and swollen and inflamed gums.

Dental problems in children
© fotolia.com
The final phase
This phase begins when the child’s first molars and incisors have grown at around 15 or 16 months.
Then the canines grow and finally the second molars complete the row of teeth.
When the child is about 3 years old, you can take a perfect photo of a smile with 20 milk teeth.
The timing of teething has hereditary backgrounds.
With 3 years the child has about 20 milk teeth. A few years after the row of teeth has grown completely, the first teeth fall out.
It usually starts when the child is about 6 years old.
They fail in the same order in which they broke out.
6 to 7 years
The first tooth starts to shake and finally falls out.
It is usually one of the lower central incisors that first erupts and fails in early childhood. The milk teeth do not actually fall out, but the underlying adult tooth presses against it and the roots of the milk tooth dissolve, so that the crown no longer has a hold.
7 to 8 years
The milk teeth usually fall out in the same order in which they broke out, the first grown tooth is also the first to loosen, starting from the center outwards.
Children’s teeth are usually wide, but in some cases a hypertrophic frenulum forms between two teeth, separating them and keeping them separate.
9 to 13 years
If the milk teeth fall out, the new teeth are initially very large. Eight new teeth (molars and premolars) occupy the entire space in the child’s mouth.
At this stage, the dentist can suggest sealing the molars.
This process involves applying resin to the teeth to prevent the formation of caries.
14 to 23 years
Up to the age of 20 you have 28 teeth, later the third molars (or wisdom teeth) appear, which increase the total number to 32.
Related Posts
-

Dental care for babies and children
Dental care for babies and children Awareness of dental hygiene and Dental care for babies and children has developed enormously. With the right dental…
-

Milk teeth caries in young children (photo) and their causes
What is important to know about tooth decay in young children In young children, tooth decay is usually much faster than in adults, and the destruction…
-

Dental care for children – health
Dental care in children Many parents are very concerned about what they should do to prevent their children from having dental problems . For this reason…
-

Casa dental, dentist for children from bonn
Especially when it comes to contact with small patients, it is very important that an experienced dentist awakens the enthusiasm for daily dental hygiene…
