bronchial asthma
Definition of bronchial asthma
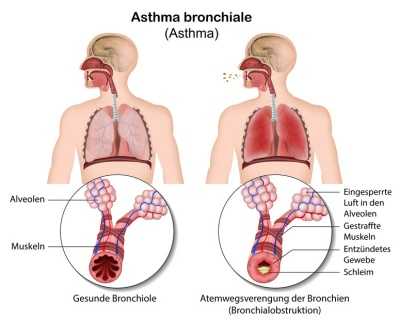
bronchial asthma The bronchial asthma is a real “common disease” that is widespread and usually results in a lasting, significant impairment of well-being. This is a seizure-related, severe respiratory distress caused by 3 changes in the bronchial system:
1. spasmodic constriction of the bronchial muscles
2. Swelling of the bronchial mucosa
3. increased production of a tough slime.
All these pathological processes have the consequence that the bronchi are severely restricted, which is especially noticeable when exhaling. By reduction of clearing of bronchi during seizure the patient does not lose the used air. Exhaling leaves more air than usual in the lungs, so that not enough fresh air can be inhaled on the next breath. As a result, the lungs become more bloated over time. The end stage is the lung distension caused by the loss of elasticity of the lung tissue (pulmonary emphysema).
The bronchial asthma, for which, in addition to the seizure character, the spontaneous regression ability of the symptoms is typical, can have many causes, an indispensable precondition being a hypersensitive bronchial system which responds to various influences with increased irritability. Even though there is often an inherited disease, bronchial asthma should not be considered a genetic disorder.
The typical asthma attack – which may be preceded by sneezing, skin or itchy back, headache, nausea, indigestion, increased urination, fatigue and anxiety – suddenly sets in after a brief feeling of tightness with severe respiratory distress. The patients feel pressure around the ribcage, as if it were pinched by iron hoops. Characteristic is the already heard at distance audible wheezing, which is interrupted by tormenting cough attacks, but only very small amounts of viscous, glassy mucus are brought to light. The difficult exhalation causes wheezing, humming and whistling noises. The patient is scared to choke. This anxiety and the general excitement additionally increase respiratory distress. During the seizure, which often occurs at night, the anxious patients sit upright with their arms propped up. Sometimes they fall desperately to the open window and gasp for air. The sweat-drenched face is pale with a blue undertone that speeds up the pulse to more than 100 beats per minute as a result of the effort. The single seizure can last only minutes, but also hours or several days. An asthma attack lasting more than 24 hours plunges the patient into acute mortal danger, as suffocation or sudden heart failure threaten. One differentiates between the following asthma forms:
1. Allergic asthma: It is triggered by substances that are either inhaled with air or supplied with food (allergy). Such substances, so-called inhalant allergens, are: house dust, mites, molds, animal hair, flower pollen of grasses, trees, shrubs, flowers and weeds in spring and summer, cereal, flour and bran dust, yeast, resins, essential oils, perfumes, spices , Green coffee, wood dust, cotton dust, kapok, flax, hemp and jute, plastics, solvents, detergents. The following asthma-causing allergens can be added to the diet: eggs, milk, dairy products, chocolate, fish, shellfish, meat, tomatoes, strawberries, nuts, honey, foods and beverages containing artificial colors and preservatives.
Allergic asthma dominates in childhood and adolescence; it is losing importance beyond the age of 45. Not infrequently, the patients already suffer from the first onset of another allergic disease, such as hay fever, an allergic conjunctivitis, eczema, etc. The allergic asthma is the only asthma form in which the cause, if persistently researched, clear can be determined. Therefore, a causal treatment is possible: First and foremost is the avoidance of the triggering factors, which may even be a career change may be required. Another method of alleviating hypersensitivity is the so-called desensitization: In this case the patient is injected with the allergen – it has to be determined beforehand by extensive skin tests – the smallest amounts which just cause a slight reaction. Subsequently, the doses are gradually increased until finally the insensitivity of the patient is reached.
2. Asthma due to chemical and physical stimuli: Road and coal dust, exhaust gases, kitchen fumes, fog, cold, humid and central heating air and – to a particularly high degree – cigarette smoke, if they are inhaled constantly lead to dysfunction of the respiratory system and damage to the bronchioles. This can also trigger asthma attacks.
3. Exercise asthma: It is especially common in children, especially when running and climbing stairs, rarely when cycling and almost never when swimming. The respiratory distress sets in 2-10 minutes after the end of the load. The complaints usually resolve within 20-30 minutes. In asthmatic children, the preventive inhalation of an asthma remedy before a special effort is reliable.
4. Painkiller’s asthma: It is caused by substances that are present in various pain, fever, inflammation and rheumatism. Breathing difficulties occur 10 minutes to 1 hour after ingestion of the least amount of the drug in question.
5. Mental AsthmaPsychiatric factors – anxiety, anger, conflict, joyful excitement – are triggered in patients with hypersensitive bronchial systems, although it should be noted that such psychological factors only have a formative and modulating function in asthma. A physically perfectly healthy person can never become an asthmatic by mental influences alone.
6. Asthma with no apparent external cause: This form is also called infectious asthma, because in some cases there is a connection with respiratory infections (bronchial system, paranasal sinuses). When asthma begins beyond the age of 30, more than 90 percent of cases are non-allergic asthma. In addition to the therapeutic options mentioned in allergic asthma, there is only symptomatic therapy for all other forms. For this purpose, means are used to prevent and treat the spasms of the bronchial muscles; Means for dissolving and liquefying the slime; Antibiotics for combating respiratory tract infection; Corticosteroids (cortisone) to control inflammatory processes. Asthma drugs can be given in a variety of preparations; Inhalation with the help of dosing aerosols and, more recently, also with extremely pulverized substances (aerosol therapy) is very well proven. Supportive are breathing exercises, connective tissue massage, relaxation exercises, psychotherapy as well as a spa and climatic treatment.
For sick people with moderate asthma attacks and good medical attitudes, the long-term perspective is good. However, a severe asthma attack can also be fatal. The long-term prognosis depends on whether irreparable damage occurs in the course of the disease, such as a lung flatulence or a cor pulmonale.
General rules of conduct for patients with asthma:
1. Smoking must be stopped.
2. All identified as triggers of asthma substances must be avoided at home, at work and on vacation.
3. Colds, especially respiratory infections, should be avoided if possible. Cold air is poison for the asthmatic. Highly recommended is the annual flu vaccine.
4. Easy exercise is useful. Heavy physical effort and competitive sports, on the other hand, should be avoided.
5. Recommended sports are: swimming, hiking, rowing and paddling, as well as archery with its harmonious interplay between tensing and loosening. Cycling and running are less affordable. In winter sports, the preventive use of a dosing aerosol is recommended because of the cold air effect.
6. In addition to breathing exercises, all kinds of relaxation exercises – especially autogenic training and yoga – are recommended.
7. Cheap holiday areas are the high mountains and the sea, especially the North Sea islands. A pollen-free climate guarantees cruises on the high seas as well as the dry, warm desert climate.
8. Beneficial are cures in an asthma spa.
9. The attitude of the patient is decisive for the success of the treatment; this must be based on the »trust principle«:
Related Posts
-

Fever, febris, medical lexicon, learn online with lecturio
fever Definition fever also known as: Febris fever Body temperature is maintained at a normal level by a mid-brain control center, which varies between…
-

Cystic fibrosis, cystic fibrosis, medical lexicon, lecturio
Cystic Fibrosis Definition of cystic fibrosis also known as: cystic fibrosis Cystic Fibrosis Hereditary enzyme disease, in which a tough mucus is…
-

Measles, morbilli, medical lexicon, learn online with lecturio
measles Definition of measles also known as: Morbilli measles The infection with measles – the virus is a virus – takes place almost exclusively from…
-
Bronchial asthma – causes, symptoms & treatment
bronchial asthma bronchial asthma or colloquial only asthma is a chronic inflammation of the respiratory tract. Cough attacks, shortness of breath and…
