Cancer in children has been occurring in the old federal states since 1980 and also in the new federal states since 1991 systematically in the nationwide German Childhood Cancer Registry at the Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz registered. Since 1988, the old federal states have assumed a sufficiently high coverage for all diagnostic groups except the tumors of the central nervous system. The Incidence increased from 1980 to 1988 is on the Initial phase of register work Due to the inclusion of therapy studies in the reporting system, a high level of completeness was recorded from the start for some diagnostic groups.
How common is cancer in children?
In Germany fall ill around 1800 children under the age of 15 annually of malignant new growths. Thus lies the annual incidence of childhood malignancies at 14.7 per 100,000 children under 15 years of age. The observation of the temporal development of the incidence gives no indication of an increase or a decrease in the disease rates.
Since the start of registration in the new federal states, an adjustment to the incidence determined for the old federal states has been observed after an initially significantly lower rate of new cases. The Proportion of children with cancer in all cancer patients is low. He is less than 1 percent. However, malignant neoplasms are the second leading cause of death in children. The survival rate is 82 percent 3 years after diagnosis and 79 percent 5 years after diagnosis.
What are the most common types of cancer in children?
The most common types of cancer in children are
Leukemia in children
The most common malignant neoplasms in childhood are with 33.4 percent the leukaemias. Most common single diagnosis with 27.4 percent is the acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). The ALL is more than twice as common in the under 1 to 4 year olds as in the other age groups. Due to therapeutic success, the survival rates have fortunately increased significantly in recent years. Approximately 5 percent of all childhood malignancies acute non-lymphatic leukaemias (ANLL). The ANLL is most common among those under the age of 1. The survival rates are significantly lower than for the ALL.
What is leukemia?
Is leukemia blood cancer and is called "white blood". He arises in the bone marrow, the blood-forming organ. Acute leukemia is characterized by a explosive increase in immature white blood cells (Blasts). This happens when the normal maturation process of white blood cells is disrupted by a malfunction of the regulatory genes in the genetic material of the blood stem cells.
A proliferation of these immature cells has a displacement and reduced production of normally mature and functional red and white blood cells and the Result in blood platelets. That means: The Blood composition changes pathologically, there is a lack of healthy white blood cells (leukocytes), red blood cells (erythrocytes) and platelets (platelets).
In essence, the following are four forms of leukemia delimited from each other:
- acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
- acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
- chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)
- chronic lymphoblastic leukemia (CLL)
At the common is the ALLES. It is characterized by the fact that lymphocytes, a subgroup of white blood cells, do not mature into normal blood cells, multiply uncontrollably and spread to the bone marrow and other organs of the body. In the AML Immature granulocytes, another subform of white blood cells, multiply and spread throughout the body. Chronic leukaemias are very rare in children.
How does leukemia manifest in children?
The little patients become pale and weak. Due to the lack of red blood cells, the works Oxygen transport in the body is getting worse. This means that all organs are increasingly poorly supplied and are therefore less functional. Due to insufficiently functioning white blood cells, which are responsible for the defense against diseases, children with leukemia increasingly susceptible to infection or fever with no noticeable infection. The decreasing number of platelets responsible for blood clotting leads to one Bleeding tendency: increased nosebleeds or bruises are observed without corresponding trauma. Swollen lymph nodes for a long time or unclear bone pain can be another sign.
Treatment of leukemia in children
The treatment consists of one intensive combination chemotherapy. Today you do therapy in two stages over a Total duration of around two years. One begins with a so-called induction treatment and consolidation therapy, which is carried out over several months in a pediatric-oncology department. This high dose, combined chemotherapy usually provides, alongside the use of cytostatics (drugs to inhibit cell division), protective treatment for the central nervous system. Under certain circumstances, too Radiation to the head.

Most of the time, they are also used for support Blood transfusions and antibiotics for infections administered. The intensity of the therapy is adjusted as closely as possible to the child’s individual relapse risk in order to keep the side effects and risks as low as possible. After the inpatient stay one closes Long-term treatment (maintenance therapy) together with a resident pediatrician or family doctor. The child is then usually switched from syringes and infusions to tablets. Children who do not respond to the aforementioned therapy can also have one Bone marrow transplant.
Why does leukemia occur in children?
Genetic influences and thus the exposure of parents to harmful influences appear to be one of the risk factors for childhood leukemia not insignificant role to play. Children with Down syndrome (Mongolism) have an increased risk of developing acute leukemia. As risk factors are drugs like alkylating substances (a type of chemotherapy) and higher doses ionizing radiation (e.g. X-rays) are known, but not in the dose range used in diagnostics.
To what extent Benzene compounds and pesticides play a role in the development of leukaemias is controversial. An association between electromagnetic fields and the occurrence of leukaemias is discussed. However, researchers are currently assuming that a Cancer risk from electrosmog not proven is.
The focus is also on Hypothesis of immunological isolation, according to which children who were protected from infection in early childhood react with a particularly strong immune response when later exposed to infectious agents. This can pose a greater risk of these cells degenerating and can lead to the development of cancer.
CNS tumors in children
Central nervous system tumors (CNS tumors) are childhood the second most common cancer, at 20 percent. In international comparison, this proportion is still rather low (mainly due to under-coverage). The most common individual diagnoses are among the CNS tumors
- Astrocytomas (8.8 percent),
- primitive neuroectodermal tumors (5.0 percent) and
- Ependymomas (2.0 percent).
Malignant lymphomas in children
Hodgkin’s disease in children
This cancer is called malignant lymphoma because it is one malignant tumor disease of the lymph nodes is. The lymph nodes in the neck and head area are mostly affected. The spleen, liver and middle chest area (mediastinum) can also be affected. Male adolescents get sick somewhat more often than female adolescents. Make Hodgkin’s lymphomas 5.1 percent of all malignant diseases in children out. The chance of recovery is very good: after 5 years, 96 percent of the affected children live.
Non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas in children
Non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas (NHL) are also among them malignant diseases of the lymphatic system. In children, they occur particularly often in the neck and head area, in the upper chest and abdomen. Spleen, liver, bones and the central nervous system can also be affected. The frequency of non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas (NHL) and Hodgkin’s disease is not very different. Make non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas 6.4 percent of all childhood malignancies out. The chances of a cure are almost as good as in Hodgkin’s disease: 87 percent of the children live after 5 years.
Other types of cancer in children
Other common malignancies in children are
- the neuroblastoma (degeneration of young cells of the autonomic nervous system),
- nephroblastoma (kidney tumor),
- the germ cell tumors (starting from testes or ovaries),
- the bone tumors and
- rhabdomyosarcoma (degenerate immature muscle or connective tissue).
While the forecast for the one Nephroblastoma or germ cell tumors sick children Cheap survival rates for the other two diseases are lower.
RELATED ITEMS
-

Leukemia in children: symptoms, therapy, prognosis
Martina Feichter studied biology with an elective in pharmacy in Innsbruck and also delved into the world of medicinal plants. From there it was…
-

Introduction Leukaemias, ie cancers of the white blood cells, are among the most common cancers in children, the lower form…
-
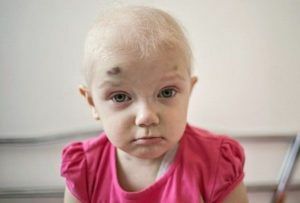
Leukemia: symptoms in children and treatment of the disease
Symptoms of Childhood Leukemia Common Signs of Childhood Leukemia Which Tests Are Performed on Childhood Leukemia? How is leukemia…
-

Leukemia, tumors Co. Why do children get cancer? December 19, 2018 at 5:19 p.m. If your child is diagnosed with cancer, it is a difficult one…
