
Leukemia in children – malignant blood disease, characterized by tumor proliferation of immature leukocyte progenitor cells. Clinical manifestations of leukemia in children can be swollen lymph nodes, hemorrhagic syndrome, pain in the bones and joints, hepatosplenomegaly, CNS lesion, etc. The diagnosis of leukemia in children contributes to a detailed blood count, sternal puncture punctured with bone marrow. The treatment of leukemia in children is carried out in specialized hematological hospitals using chemotherapy, immunotherapy, replacement therapy, bone marrow transplantation.
Leukemia in children
Leukemia in children (leukemia) – systemic hemoblastosis, accompanied by an injury to bone marrow hematopoiesis and the replacement of normal blood cells with immature leukocyte blasts. In oncohematology in children, the incidence of leukemia is 4-5 cases per 100,000. Children. According to statistics, acute leukemia is the most common childhood cancer (approximately 30%); Blood cancer most often affects children aged 2-5 years. The current problem of pediatrics can be observed in recent years, the tendency to increase the incidence of leukemia in children and the persistently high mortality.
Causes of childhood leukemia
Some aspects of the development of childhood leukemia are still unclear. At the present time, the etiological effect of radiation has been proven, oncogenic virus strains, chemical factors, hereditary predisposition, endogenous disorders (hormonal, immune) on the incidence of leukemia in children. In a child, secondary leukemia can develop after a history of radiation or chemotherapy for another cancer.
Nowadays, the mechanisms of developing leukemia in children are usually viewed from the point of view of mutation theory and the clonal concept. The DNA mutation of the hematopoietic cell is associated with the failure to differentiate at the immature blast cell stage, followed by proliferation. In this way, leukemia cells – there is nothing but clones of a mutated cell, unable to differentiate and mature and to suppress normal hemopoiesis sprouts. Get into the blood, explosive cells spread throughout the body, contribute to leukemia infiltration of tissues and organs. The metastatic penetration of blasts through the blood-brain barrier leads to infiltration of the membranes and substances of the brain and the development of neuroleukemia.
Highlighted, children with Down’s disease develop 15 times more often than other children. There is an increased risk in children with Li Fraumeni syndrome for the development of Leukemia and other tumors, Klinefelter, Whiskott Aldrich, flowering, Fanconi anemia, primary immunodeficiency (X-linked agammaglobulinemia, ataxia telangiectasia Louis-Barr et al.), Polycythemia and others.
Children’s leukemia classification
Depending on the duration of the disease, acute (up to 2 years) and chronic (more than 2 years) forms of leukemia in children. Most often in children (97%) acute leukemia. Congenital leukemia is a special form of acute leukemia in children.
Based on the morphological properties of tumor cells, acute leukemia in children is divided into lymphoblastic and non-lymphoblastic. Lymphoblastic leukemia develops with uncontrolled proliferation of immature lymphocytes – lymphoblasts – and there are three species: L1 – with small lymphoblasts; L2 – with large polymorphic lymphoblasts; L3 – with large polymorphic lymphoblasts with vacuolation of the cytoplasm. Antigenic markers distinguish 0 cells (70-80%), T cells (15-25%) and B cells (1-3%) from acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children. In acute lymphocytic leukemia in children, leukemia is more common in L1 cells.
Differentiate in a number of non-lymphoblastic leukaemias, depending on the prevalence of certain blasts, myeloblastic undifferentiated (M1), myeloblastic strongly differentiated (M2), promyelocytes (M3), myelomonoblastic (M4), monoblastic (M5), erythromylosis (M6), Megakaryocytosis (M7), eosinophil (M8), undifferentiated (M0) leukemia in children.
In the clinical course of childhood leukemia there are 3 stages, built taking medical tactics into account.
- I – acute leukemia in children; covers the period from the manifestation of the symptoms to the improvement of the clinical and haematological parameters as a result of the therapy;
- II – incomplete or complete waiver. If remission is incomplete, the blood count and clinical parameters normalize; The number of blasts in the bone marrow punctate is no more than 20%. A complete remission is characterized by the fact that the myelogram is at most 5% explosive cells;
- III – relapse of childhood leukemia. Against the background of haematological well-being, extramedullary foci of leukemic infiltration occur in the nervous system, testes, lungs, etc. organs.
Symptoms of childhood leukemia
In most cases, the leukemia clinic develops gradually and is characterized by non-specific symptoms: child fatigue, sleep disturbance, reduced appetite, ossalgia and arthralgia, unmotivated fever. Sometimes childhood leukemia suddenly manifests with poisoning or hemorrhagic syndrome.
In children who suffer from leukemia, pronounced pallor of the skin and mucous membranes; Sometimes the skin turns yellow or yellowish. Due to the leukemia infiltration of the mucous membranes in children, gum infections, stomatitis, tonsillitis often occur. Leukemic hyperplasia of the lymph nodes manifests lymphadenopathy; Salivary glands – sialadenopathy; Liver and spleen – hepatosplenomegaly.
Hemorrhagic syndrome is typical for the course of acute leukemia in children, characterized by bleeding in the skin and mucous membranes, hematuria, nasal, uterus, gastrointestinal, pulmonary bleeding, bleeding in the joint cavity, etc. The natural companion of acute leukemia in children is an anemic syndrome , caused by inhibition of erythropoiesis and bleeding. The severity of anemia in children depends on the degree of proliferation of blasts in the bone marrow.
Cardiovascular disorders in children with leukemia can be expressed through the development of tachycardia, arrhythmias that expand the limits of the heart (after chest X-ray), diffuse myocardial changes (after ECG), low emissions (after echocardiography).
Intoxication syndrome, accompanying leukemia in children, occurs with considerable weakness, fever, sweating, anorexia, nausea and vomiting, hypotrophy. The manifestations of immunodeficiency syndrome in children with leukemia are the stratification of infectious-inflammatory processes, which can be difficult, threatening course. Child death, leukemia, often due to severe pneumonia or sepsis.
An extremely dangerous complication of leukemia in children is leukemia infiltration of the brain, meninges and nerve trunks. Neuroleukemia is accompanied by dizziness, headache, nausea, diplopia, stiff neck. When the substance of the spinal cord infiltrates, paraparesis of the legs can occur, sensory disorders, pelvic disorders.
Diagnosis of leukemia in children
The pediatrician plays the leading role in the primary detection of leukemia in children; The further examination and treatment of the child is carried out by a pediatric oncohaematologist. Laboratory methods are the basis of the diagnosis of leukemia in children: peripheral examination of blood and bone marrow.
In children with acute leukemia there are characteristic changes in the general blood test: anemia; Thrombocytopenia, reticulocytopenia, high ESR; Leukocytosis of various degrees or leukopenia (rare), blastemia, disappearance of basophils and eosinophils. A typical symptom is the phenomenon of "leukemic failure" – lack of intermediate forms (young, Bandker, segmented leukocytes) between mature and blasts.
Star puncture and myelogram study are mandatory in the diagnosis of leukemia in children. The decisive argument for the disease is the content of blasts from 30 years% and above. In the absence of clear data on leukemia in children from a bone marrow study, use of trepanobiopsy (iliac puncture). To determine the different variants of acute leukemia in children, cytochemical tests are carried out, immunological and cytogenetic studies. To confirm the diagnosis of neuroleukemia, a consultation with a pediatric neurologist and a pediatric ophthalmologist is carried out, examination of the lumbar puncture and cerebrospinal fluid, x-ray of the skull, ophthalmoscopy.
Auxiliary diagnostic values include ultrasound of the lymph nodes, ultrasound of the salivary glands, ultrasound of the liver and spleen, ultrasound scrotum in boys, chest X-ray, CT in children (metastases in different anatomical regions can be seen). The differential diagnosis of childhood leukemia should be done with a leukemia reaction, observed in severe forms of tuberculosis, whooping cough, infectious mononucleosis, cytomegalovirus infection, sepsis and reversible transient nature.
Treatment of leukemia in children
Children with leukemia are hospitalized in specialized oncology and hematology facilities. To avoid infectious complications, the child is placed in a separate box, conditions in which as close as possible to sterile. Much attention is paid to nutrition, which must be complete and balanced.
The basis of the treatment of leukemia in children is polychemotherapy, complete eradication of the leukemia clone. Treatment protocols used in acute lymphoblastic and myeloblastic leukaemias differ in combination chemotherapy, their doses and routes of administration. The gradual treatment of acute leukemia in children includes achieving clinical and hematological remission, its consolidation (fixation), maintenance therapy, prevention or treatment of complications.
In addition to chemotherapy, active and passive immunotherapy can be administered: introduction of leukemia cells, BCG vaccine, smallpox vaccine, interferon, immune lymphocytes, etc. Promising methods for the treatment of leukemia in children are bone marrow transplants, umbilical cord blood, stem cells.
Symptomatic therapy in children with leukemia includes transfusions of red blood cells and platelets, hemostatic therapy, Antibiotic treatment of infectious complications, detoxification measures (intravenous infusion, hemosorption, plasma sorption, plasma exchange).
Prognosis of leukemia in children
The prospects for the development of the disease are determined by many factors: age of leukemia, cytoimmunological variant, stage of diagnosis and t. d. The worst prognosis should be expected in children, patients with acute leukemia before the age of 2 years and older than 10 years; with lymphadenopathy and hepatosplenomegaly, as well as neuroleukemia at the time of diagnosis; T and B cell variants of leukemia, blasts hyperleukocytosis. The prognostically favorable factors are acute lymphoblastic leukemia L1, early treatment, quick remission, and the age of children from 2 to 10 years. Girls with acute lymphoblastic leukemia have a slightly higher chance of recovery than boys.
The lack of a specific treatment for leukemia in children is accompanied by 100% lethality. Against the background of modern chemotherapy, there is a five-year relapse-free course of leukemia in children aged 50-80 years. We can talk about the likely recovery after 6-7 years without relapse. To avoid provoking a relapse, physiotherapy is not recommended for children, climate change. The vaccination prophylaxis is carried out in an individual calendar taking into account the epidemic situation.
RELATED ITEMS
-
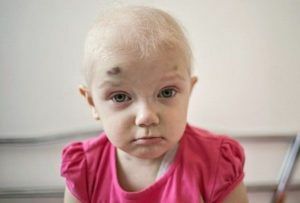
Leukemia: symptoms in children and treatment of the disease
Symptoms of Childhood Leukemia Common Signs of Childhood Leukemia Which Tests Are Performed on Childhood Leukemia? How is leukemia…
-
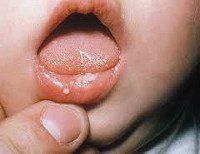
Herpes stomatitis in children – causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Herpes stomatitis in children is an acute inflammatory lesion of the oral mucosa caused by the herpes simplex virus. Herpes stomatitis…
-

Herpes angina in children – causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Herpes angina in children is an acute, virally induced lesion of the pharyngeal lymphoid tissue caused by Coxsackie and ECHO viruses….
-

Influenza in children – causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Influenza in children is an acute infection from influenza A, B, C; characterized by respiratory infection, intoxication and high…
