
Professional teeth cleaning (PZR)
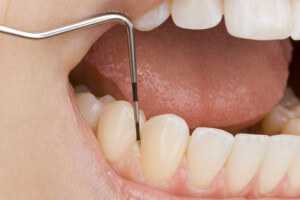
There are places in the mouth where the toothbrush can not adequately align or where plaque develops due to inadequate cleaning techniques. The so-called PZR is a thorough cleaning of the teeth in a dental practice, usually performed by a trained Prophylaxeassistentin or a dental hygienist.
In the process, dental plaque, tartar and concrements are removed and the dentition is thoroughly checked.
Finally, the teeth are polished to make it difficult for bacteria to colonize and fluoridated. Mostly also a guide to better dental care and oral hygiene is included. The treatment lasts about one hour and should be done about every six months. Inform yourself about a professional cleaning of teeth in casting.
Additional information on professional teeth cleaning
Protecting your teeth from caries (tooth decay) and periodontitis (inflammation of the periodontium) into old age is a viable goal if prophylactic (preventative) measures such as consistent home-based dental care and regular professional teeth cleaning (PZR) go hand in hand with the dentist.
Domestic oral hygiene makes areas such as the interdental spaces (interdental spaces) and the retromolar spaces (behind the last molars) significantly harder to catch than the chewing, outside and inside surfaces of the teeth. But accumulates plaque (microbial plaque) over several days, a gingivitis (gingivitis) is the result, which can turn into a periodontitis on prolonged chronic course again. In addition, cariogenic bacteria in the plaque endanger tooth health through tooth decay.
While a gingivitis can be reversed by improved and ambitious plastering technique, this does not help any further, if dental plaque has solidified by accumulation of minerals first to tartar (above the gum edge) or even concrements (tartar below the gum edge). Even solid color deposits that arise when you enjoy coffee, tea, nicotine or the like, are difficult to eliminate with the home oral hygiene technology. This is where the professional tooth cleaning (PZR), which in the dental practice usually by trained professionals (dental prophylaxis, dental assistant, dental hygienist) is performed.
The combination of good dental care and PZR can be caries (tooth decay, bacterial destruction of hard tissues), gingivitis (gingivitis) and periodontal disease (tooth inflammation) effectively and lifelong prevent.
Professional Dental Cleaning (PZR) includes:
- the removal of soft and hard deposits on the enamel and possibly exposed tooth roots supragingival or gingival (above or in the area of the gingival margin)
- the cleaning of the interdental spaces (interdental spaces)
- removal of biofilm (plaque, microbial deposits)
- the surface polish of the teeth
- suitable local (local) fluoridation measures for caries protection
- Training / oral hygiene exercises and / or use of oral hygiene aids
- Indications (indications)
The PZR is used:
- for the removal of supragingival tartar (above the gingival margin) and concretions in the clinically achievable subgingival area (in the upper part of the periodontal pocket)
- for the treatment of bacterial gingivitis
- for removal of superimposed tooth discolorations
- Halitosis (halitosis)
- as part of a periodontal initial treatment (before further measures for the treatment of a periodontal inflammation)
- for maintenance therapy after treatment of periodontitis (tooth inflammation)
- in the context of a recall (a pre- or aftercare treatment)
The intervals of a recall (the follow-up appointments) are to be determined individually for each patient and are usually between three and six months. In particular, if supportive periodontal therapy for long-term maintenance (UPT) is required following successful periodontitis therapy (tooth-brush inflammation, eg surgically or with the Vector® method), close recall will be indicated to prevent re-adherence of subgingival calculus (tartar below the edge of the gum in the periodontal pockets) from the outset to prevent and in the biofilm a shift in the germ composition towards apathogenic germs (without disease value) to favor.
In the course of a PCR, bleeding may occur, especially in the presence of gingivitis or periodontitis. Since the integrity of the gingival tissue is injured, bacteremia (swamping germs into the bloodstream) is the result. This results in the following contraindications:
-
necrotizing and ulcerous gingivitis (NUG) and periodontal disease (NUP): in this case, soft deposits are initially only very carefully with Chlorhex >
- Cardiac risk history (of the heart): Antibiosis for endocarditis prophylaxis (prevention of bacterial inflammation of the heart) must be performed in certain cases.
- Weakened immune defense: Again, the treatment is possibly under shielding by an antibiotic possible.
- Pacemaker of older design: here should in the PZR due to possible interference on the use of magnetostrictive ultrasound devices (magnetostriction: deformation of magnetic substances) such. B. the Cavitron® be waived.
- Adolescent teeth with unfinished enamel ripening: after the tooth has broken through, the enamel still requires a long period of time (about three years), depending on the oral environment, to reach its final hardness. a. by the incorporation of fluoride, phosphate and calcium ions from saliva. In this phase, ultrasound, powder jet and polish pastes can lead to damage to the tooth structure.
- White spots (less mineralized enamel with incipient caries): here, too, the enamel does not have the necessary hardness to withstand the cleaning measures.
Before the procedure
- Intraoral inspection (examination of the oral cavity): Before the procedure, an oral hygiene status is created, if necessary, which reproducibly documents the inflammatory condition of the gingiva (gingiva) and the plaque infestation of the teeth using so-called indices (= collection of bleeding and plaque index).
- By demonstrating bacterial plaque with colored plaque levelers (substances that color the plaque and make it more visible), the patient can be motivated in advance and made aware of hygiene deficits.
- For disinfectant protection, a disinfecting mouthwash (eg, 30 seconds with 0.2% chlorhexidine) is used to reduce the number of microbes in the droplet spray created during ultrasonic cleaning.
- The dentist will pre-contour and polish excess filling margins and other plaque trapping sites (sites where the microbial coating may adhere well due to morphology).
- First, the teeth are freed of calculus with the help of ultrasonic vibrations (eg Vector Scaler) and / or classical hand scalers.
- Alternatively, there is the possibility of scaling with powder blasting equipment (eg Air-Flow® system or ProphyFlex®), which, however, are used particularly effectively for the removal of stubborn dark discolorations caused by foods such as coffee, tea, red wine or Nicotine arise. Also, the biofilm (plaque, microbial deposits) will be eliminated at the latest in this operation.
- (Supra) gingival plaque removal (below the gums): This is done if necessary by mechanical methods and with hand instruments.
- Polishing of the tooth surfaces: The surface polish of all tooth surfaces, including the interdental spaces (interdental spaces), is then carried out with nylon brushes and / or rubber particles, which are loaded with polish pastes in decreasing abrasiveness (roughness).
- Finally, the teeth are treated for caries prophylaxis (prevention of tooth decay) with fluoride in the form of rinses, paints, gels or fluids.
- Oral Hygiene Instruction: Oral hygiene training and / or oral hygiene use
- Recall appointments: depending on the individual risk classification
- The removal of firmly adhering tartar or concrement residues in hard to see areas such. B. Root catching can be problematic.
- Incorrect use of cleaning instruments and materials such as coarse polish pastes or powder jet, the removal of hard tooth substance, especially if this is pre-damaged (initial caries, white spots) or not yet mature, can not be excluded.
- Metal surfaces (eg, cast crowns and inlays) may become shiny due to coarse-grained polish pastes or powder spray.
- Ceramic veneers can be damaged by the use of ultrasound.
- Composite fillings can be removed by coarse-grained pastes or powder jet.
Related Posts
-
Professional teeth cleaning for well-groomed and whiter teeth
Professional teeth cleaning for well-groomed and whiter teeth It is always advisable to perform a tooth cleaning before whitening your own teeth. Whether…
-

Prophylaxis professional dental cleaning frankfurt, dental dentist, dental dentist frankfurt
Professional teeth cleaning in Frankfurt Why is a professional tooth cleaning really useful? No matter how often you brush your teeth, you will never be…
-

Root canal treatment – dentist carina sell
Root canal treatment of the dental practice Carina Sell in Gießen Root canal treatment The root canal treatment is an endodontic treatment (treatment of…
-

What is the benefit of a professional tooth cleaning? Dentist ulm hans-georg stromeyer
Professional teeth cleaning (PZR) How teeth get their shine again plaque make the surface appear dull and dull. Nicotine, tea, coffee, red wine, cola and…
